Lion-Tailed Macaque | Ias Banenge
Context:
Recently, Lion-tailed macaque has been sporadically spotted by conservationists in the forests of Nadugani, shared by the Nilgiris district in Tamil Nadu and Nilambur in Kerala.

Relevance:
GS III: Environment and Ecology
READ MORE- Key Highlights of the 15th BRICS Summit |Ias Banenge
Dimensions of the Article:
- Lion-tailed Macaque
- Conservation Status
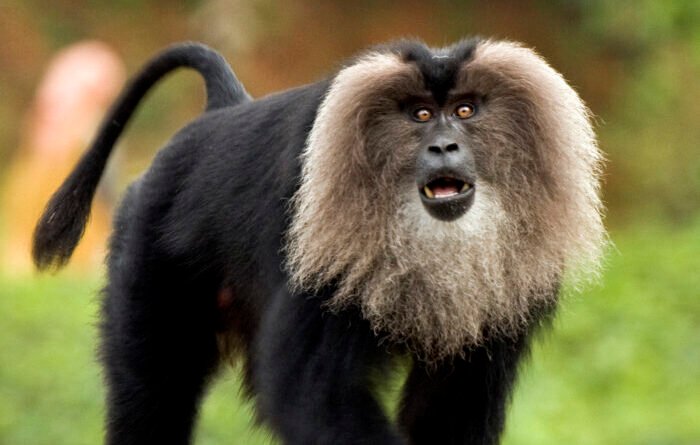
Lion-tailed Macaque:
- Species Classification: The Lion-tailed macaque (Macaca silenus) belongs to the category of Old World monkeys.
- Distinctive Male Behavior: A unique trait of this species is that males establish the boundaries of their home territories through vocal calls.
- Rich Communication System: These macaques employ a communication system featuring as many as 17 distinct vocalizations.
Appearance
- Grey Mane: They are recognizable by the gray mane encircling their face.
- “Bearded” Monkeys: They are sometimes referred to as bearded monkeys due to their distinctive facial hair.
- Tail Characteristics: The Lion-tailed macaque’s name is derived from its lion-like tail, which is lengthy, slender, and adorned with a tuft.
Habitat
- Exclusive to India: This species is found exclusively in India.
- Endemic Range: Lion-tailed macaques are native to the fragmented rainforests of the Western Ghats, particularly in the states of Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu.
Threats
- Habitat Destruction: The primary threat to the Lion-tailed macaque population is the degradation and loss of their rainforest habitat.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Status: Listed as Endangered on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List.
- CITES Listing: Included in Appendix I of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), which offers the highest level of protection.
- Wildlife Protection Act: In India, the Lion-tailed macaque is categorized under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, granting it legal protection.
-Source: The Hindu




Pingback: What are Urban Cooperative Banks? Ias Banenge